COMPUTATIONAL FLUID
DYNAMICS
R + D
TOPIC
CFD, Case Study, Naturally Cross Ventilated
DESCRIPTION
Introduction of computational analysis to architectural precedence, invetigating form and design elements focused on the dicreet use of natural ventilation through negative and postive pressure pockets.
YEAR
2021
TEAM
Kyle Koops
KEY WORDS
CFD, Simulation
CFD


The simulation above was undertaken as part of the initial research for development of a new type of architecture following the Covid-19 pandemic. The Torre Cuba proved an excellent example of a naturally ventilated mid-rise, effectively utilizing negative and positive pressure pockets supported by exhaust through the stack effect.
Elements of the design were studied and carried through into the development the projects below.
EXTERNAL VOLUME STUDIES

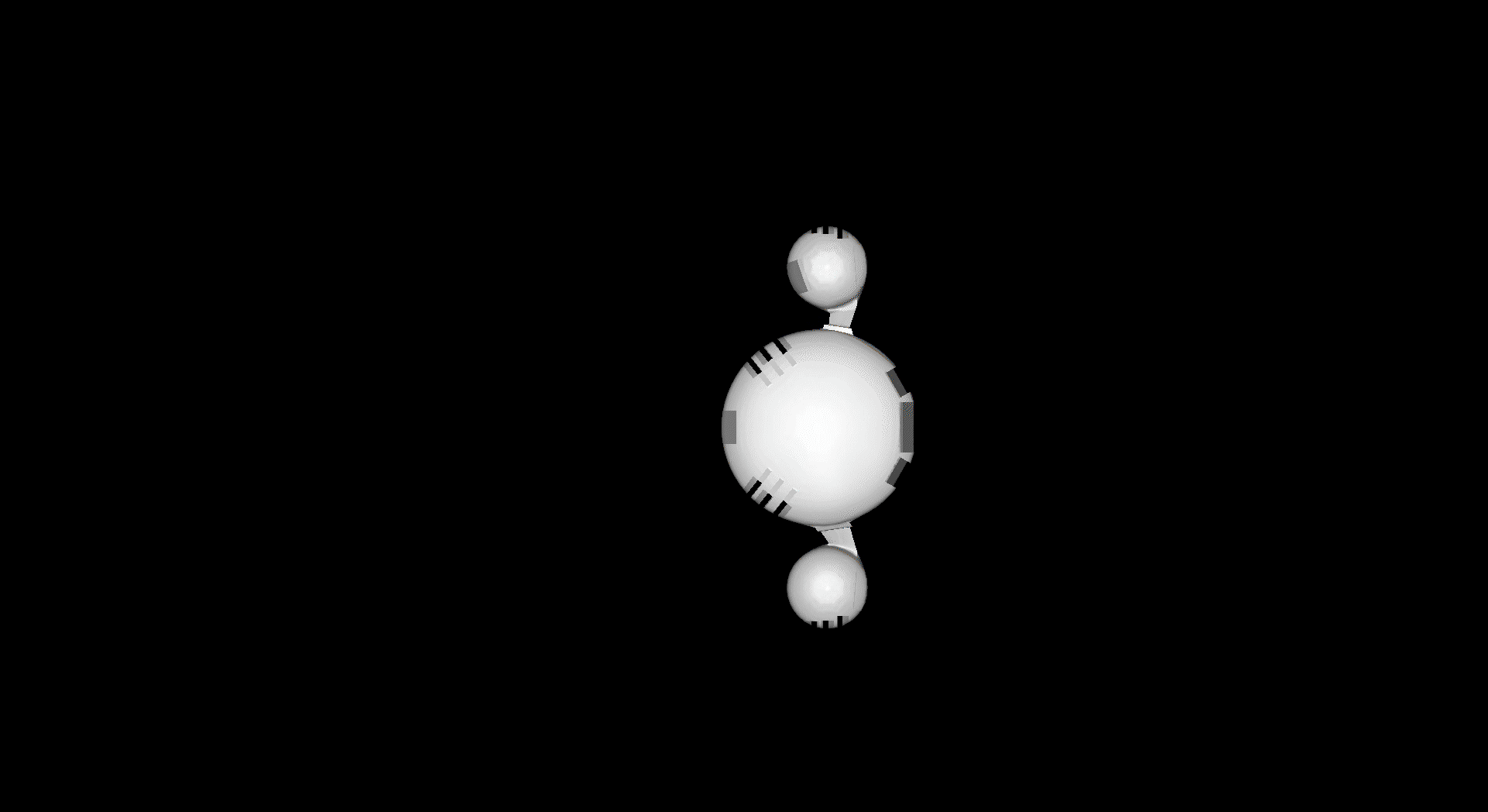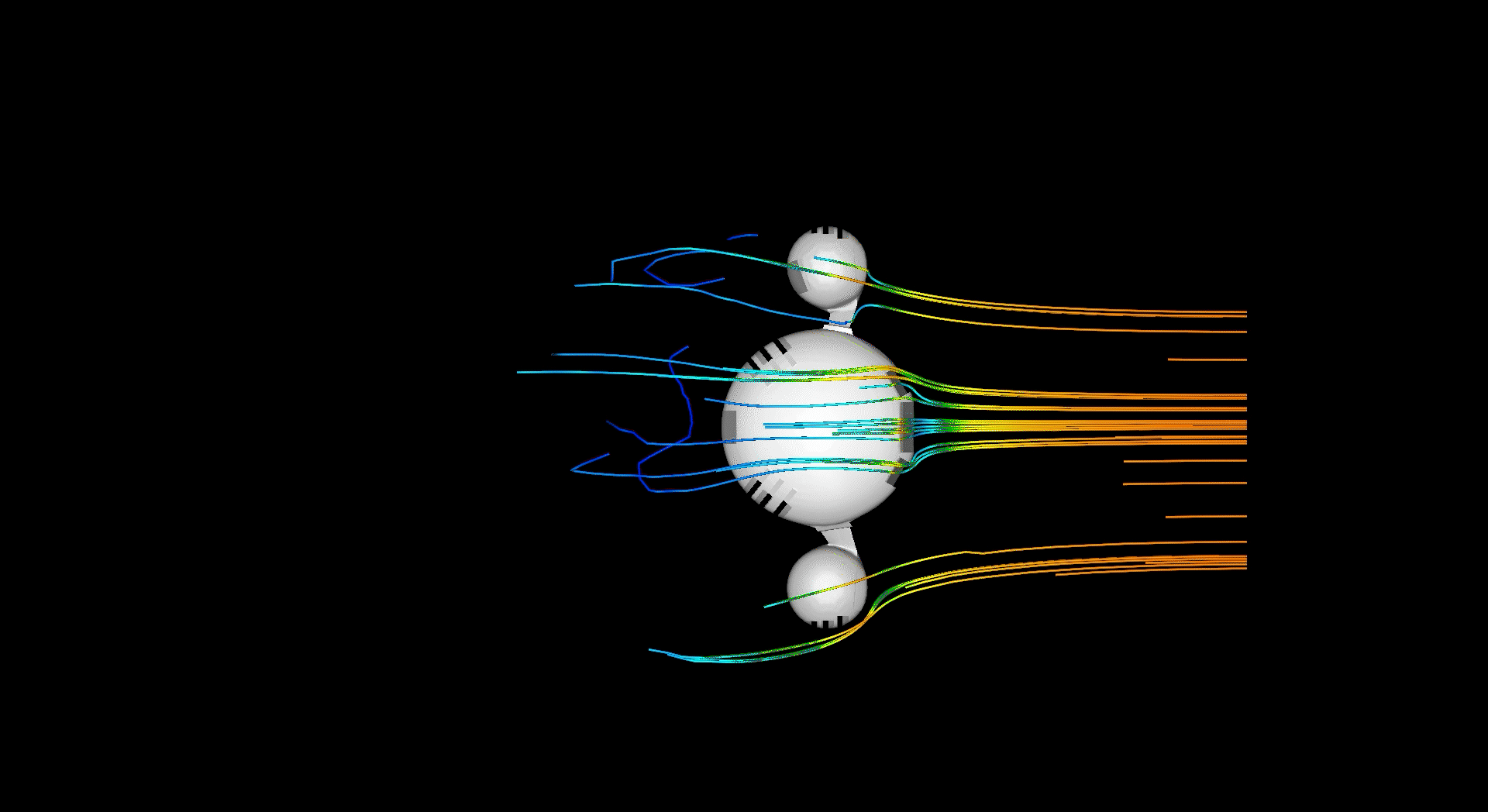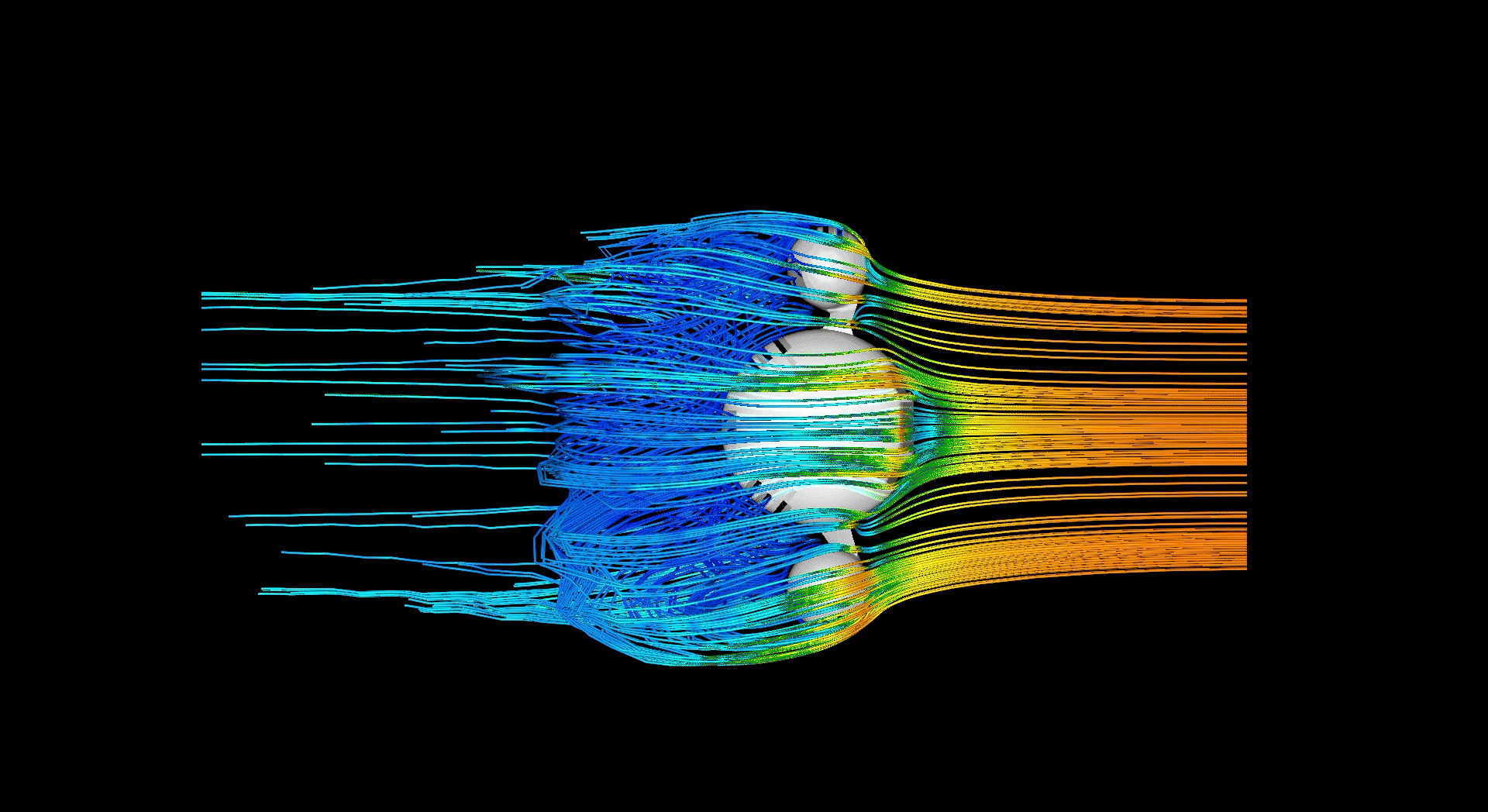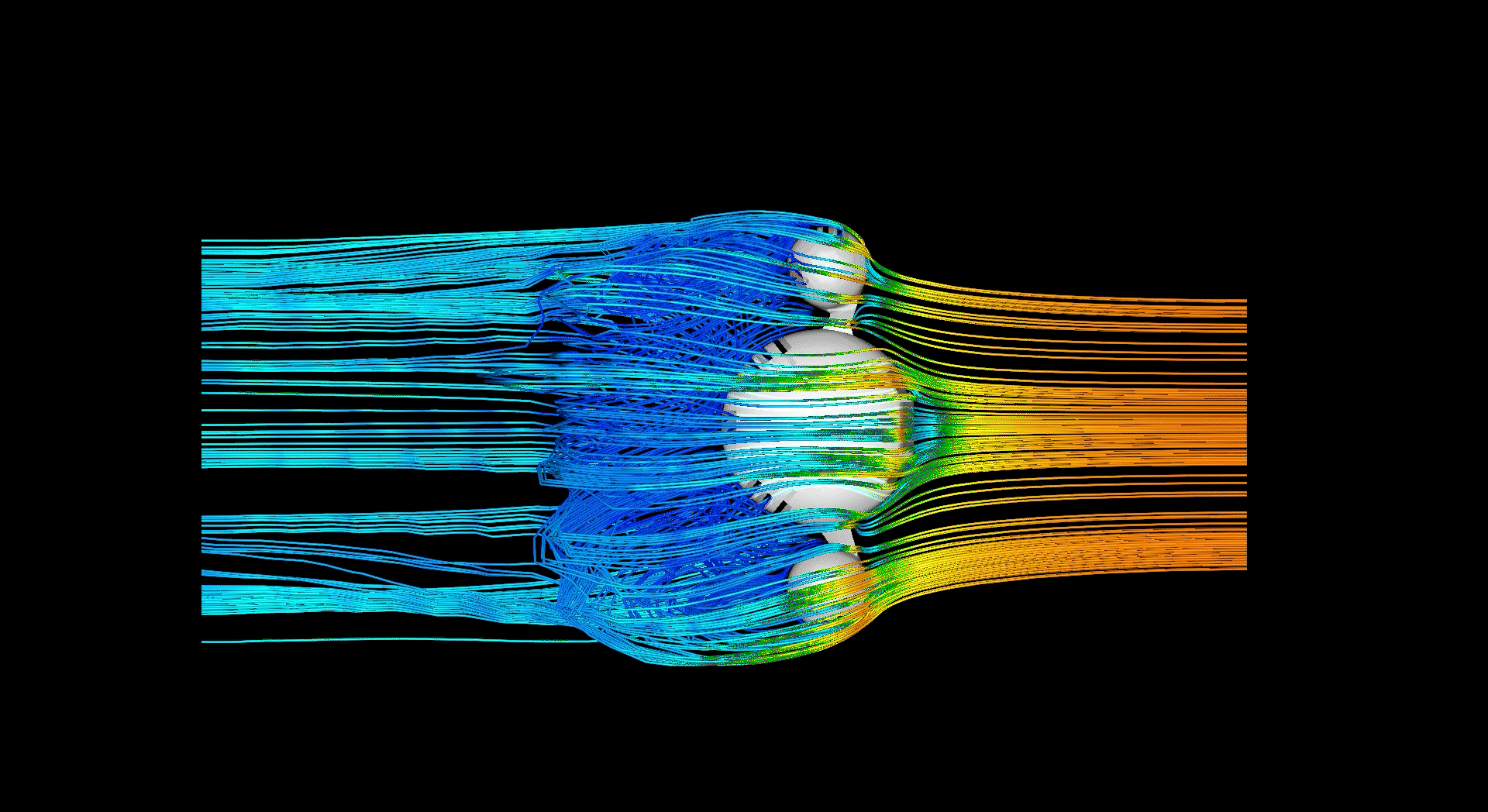
Massing studies investigating how channels could be used to manipulate directon and accelleration/decelleration of air, preparing to transfer it between the external and internal barrier.
INTERAL VOLUME STUDIES
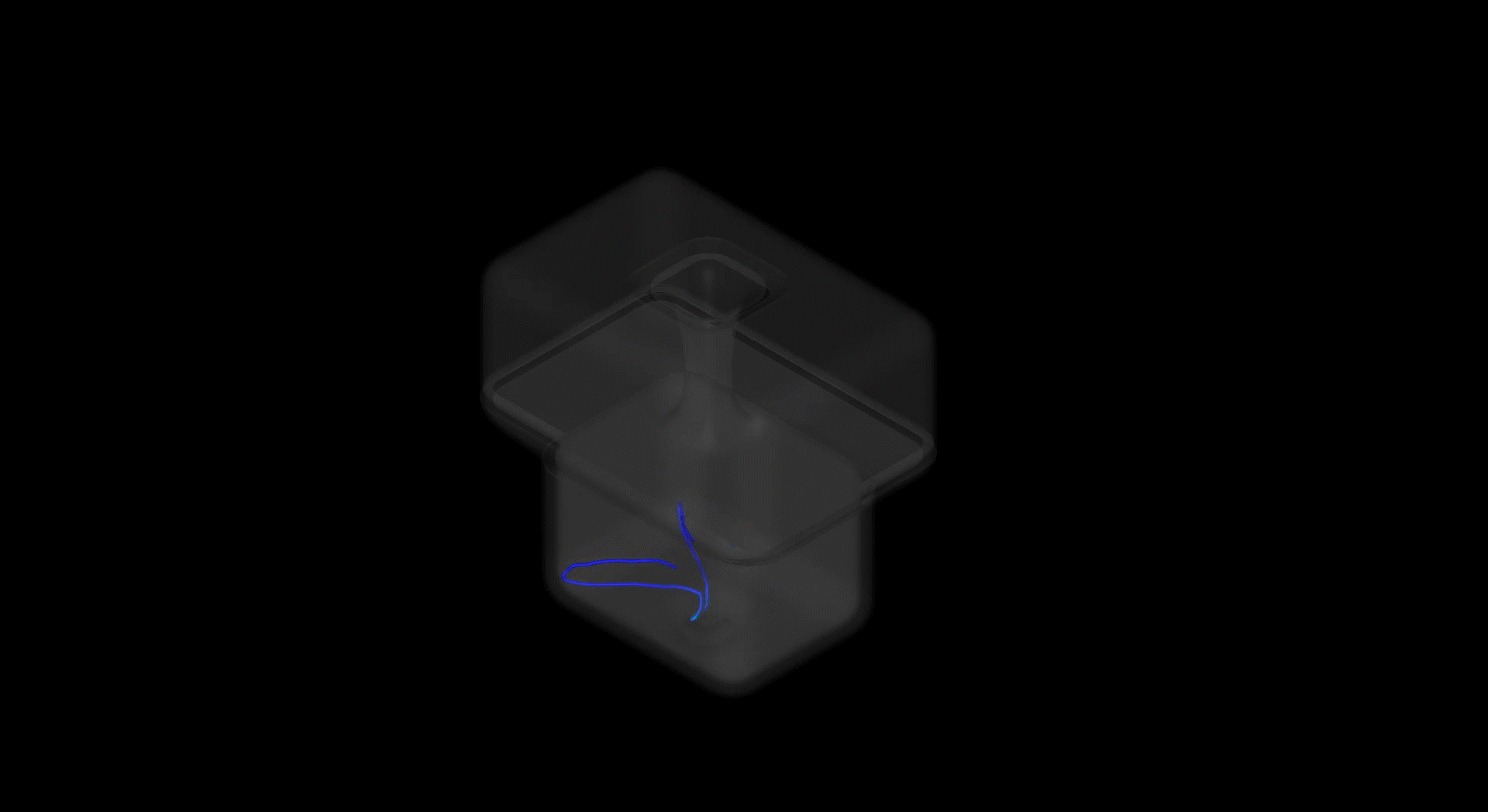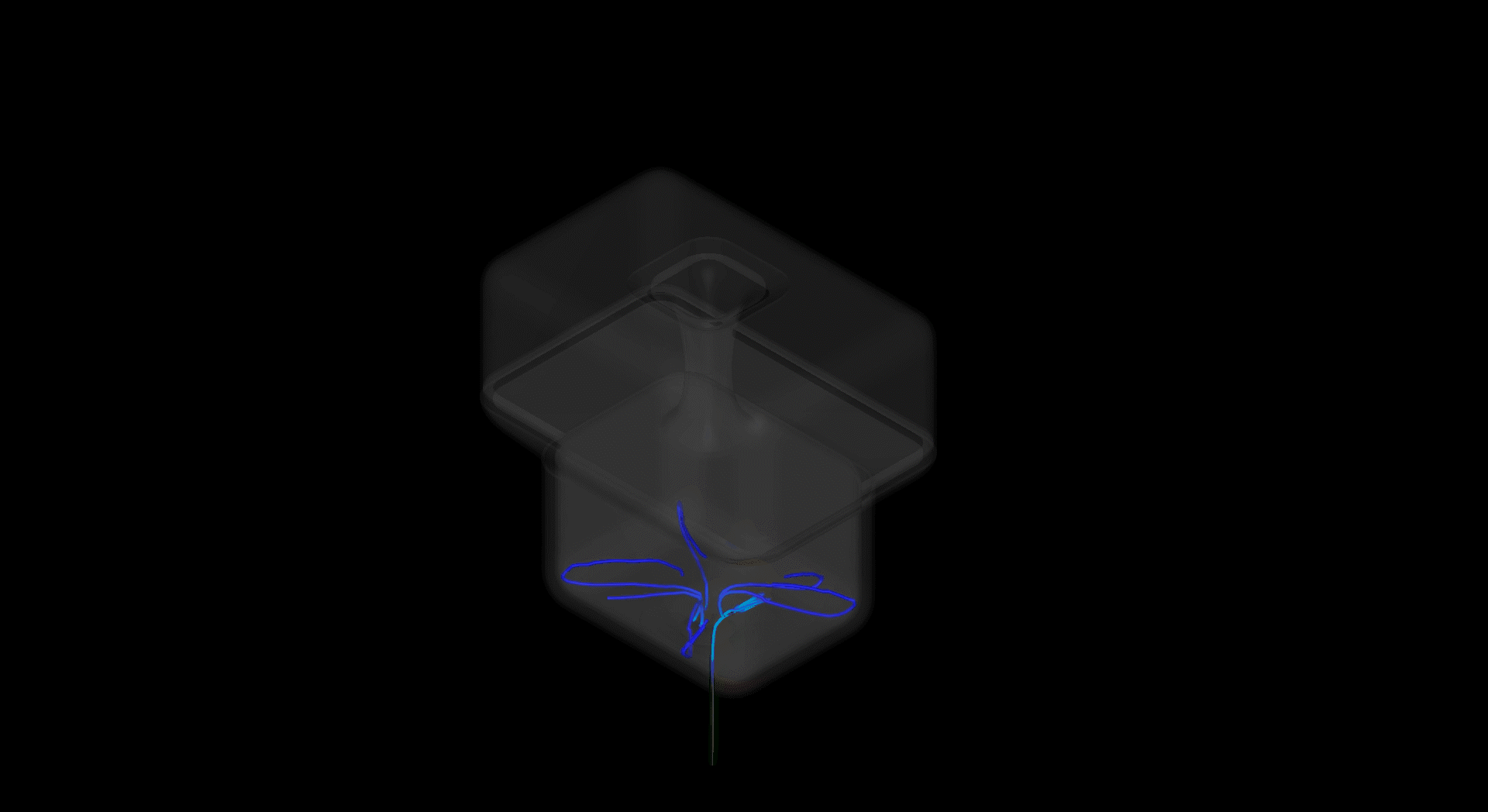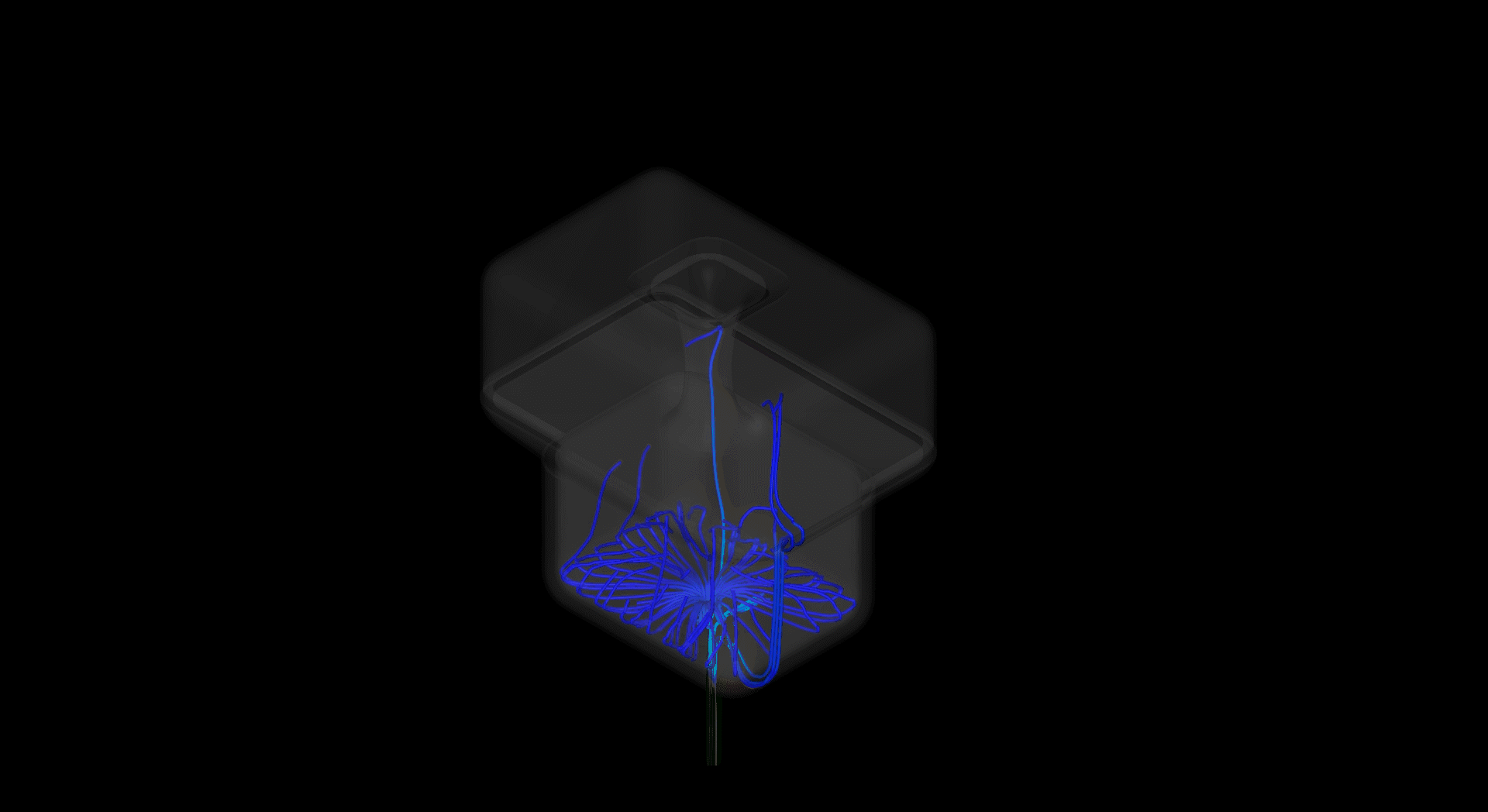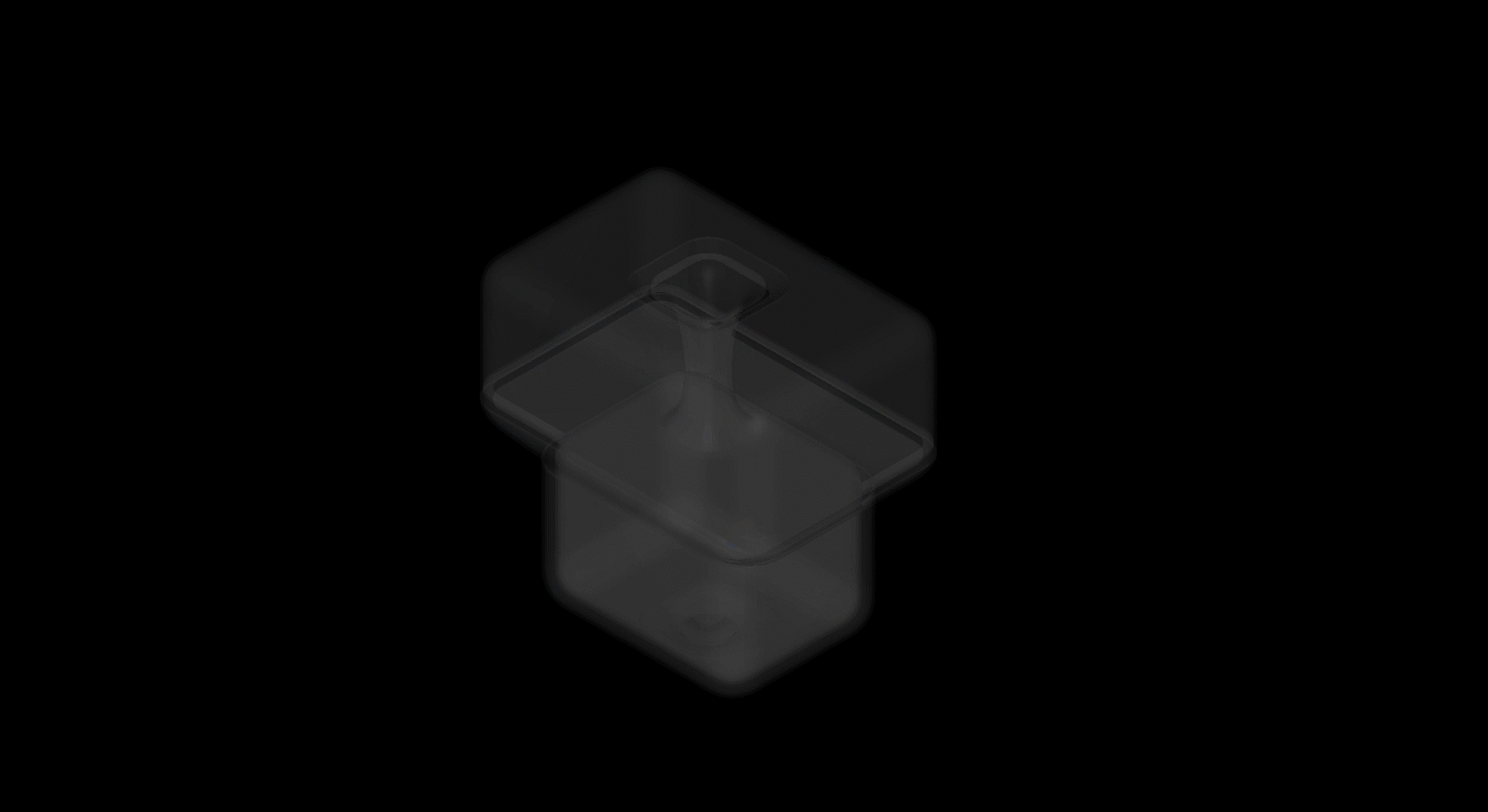
Interally, investigations were undertaken to study how air could be used to efficiently ventilate high-density spaces.
While it is reletively simple to exchange the air in a space, the challenge was maintaining comfort for the user during exchange. Having air blown directly at you cannot be maintained, in the above example a floating floor plate creates a high pressure zone, and from here the air is forced through smaller channels withing the walls until exhausted through the roof.
As the air is transferred from the intial chamber beneath the floor, to subsequent smaller chambers acceleration occurs, this creates a suction effect which pulls stationary air from the occupied space.